Did you know that among the top 12 animals, bees can help keep us safe from wandering elephants? Or that sharks, included in the top 12 animals, keep CO2 out of the atmosphere? The animals around us and among the top 12 animals around the world help protect us, each other, and the planet in numerous ways. Here are just a few of the top 12 animals we owe a thank you.
1 Elephants
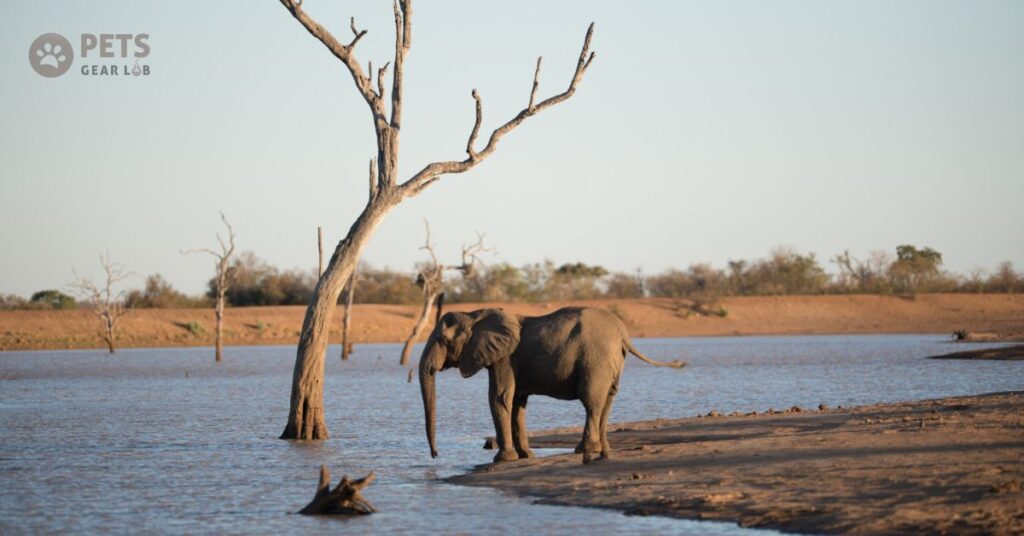

As the largest land animals on Earth, elephants play a major role in their ecosystems for various reasons. First they consume as much as 150 kilograms (330 pounds) of vegetation daily, storing significant amounts of carbon in their dung, enriching the soil as a natural fertilizer and preventing greenhouse gases from entering the atmosphere. Their dung also disperses seeds, benefiting many plants.
Second, elephants constant movement through woodlands and savannahs helps maintain their habitats. By tearing down brush and trees along their paths, they prevent overgrowth and encourage the growth of new plants by thinning out competing trees.
Third, elephants aid smaller animals by breaking branches, making food sources more accessible. Additionally, their digging for water creates watering holes, benefiting other animals unable to do so themselves.
Overall, the biodiversity elephants support provides essential resources for humans as well such as shade, fertile soil and water. By indirectly assisting other wildlife, elephants help mitigate competition between humans and animals for these vital resources.
2 Rhinos
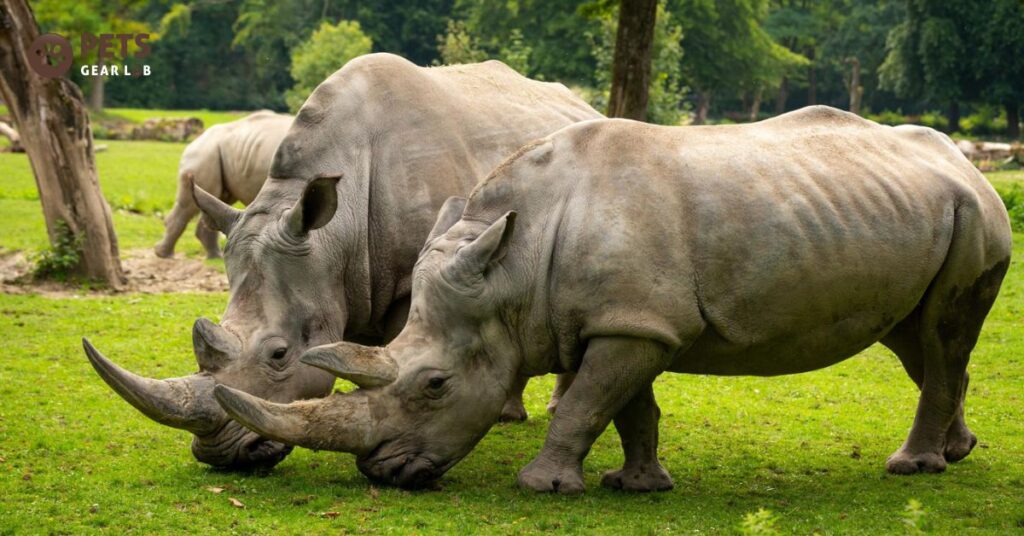

Rhinos are big plant-eating animals that are really important for the plants where they live. People who live near rhinos need the things these animals help with, like water and soil. When rhinos roll around in mud, they keep water spots open and make new ones. The mud that sticks to them helps the ground when it dries and falls off. Their poop also helps the soil. The areas where rhinos live, like grasslands, take in carbon from the air which is good for fighting climate change.
3 Pangolins
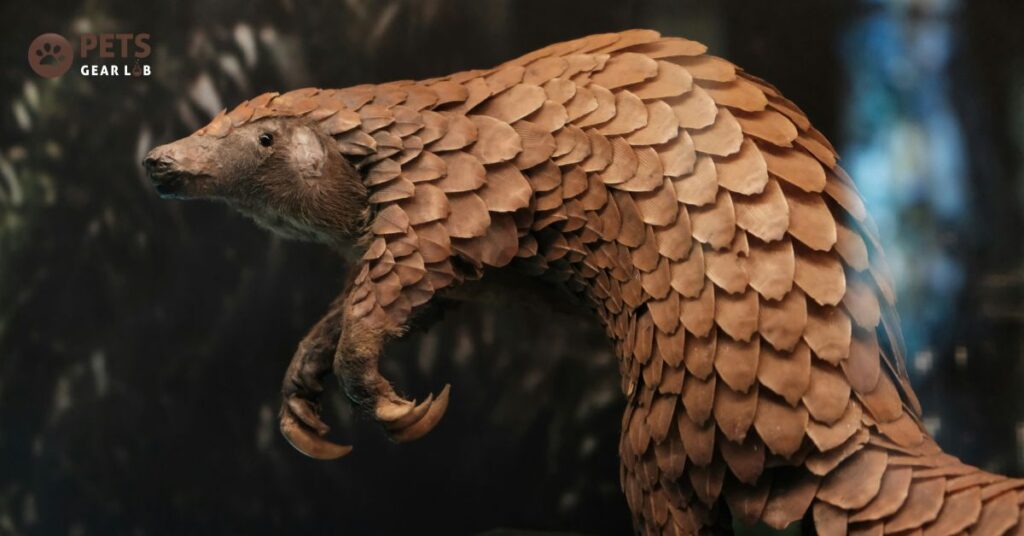

If you are not fond of ants and termites, you have the humble pangolin to thank, as it devours an impressive 70 million of them each year. This voracious appetite serves a vital purpose, preventing these insects from wreaking havoc on forest ecosystems. Using their remarkable digging abilities and long, sharp claws, pangolins excavate the soil in search of insects, inadvertently creating burrows that play a crucial role in spreading nutrients and aerating the earth. It’s no wonder they are often referred to as the gardeners of the ecosystem.
These burrows don’t just benefit pangolins they provide shelter for numerous other small animals, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the area. Additionally, pangolins contribute to the decomposition process by tearing apart decaying logs and termite mounds, facilitating the breakdown of organic and inorganic matter and promoting the cycling of minerals and nutrients throughout the forest.
In essence, pangolins offer a dual service to their environment: pest control and gardening. Despite their invaluable contributions, these shy, small and scaly mammals face an ever-present threat from poaching. Organizations like the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW) are tirelessly working to protect these unique creatures and ensure their survival for future generations to appreciate and admire.
4 Giraffes
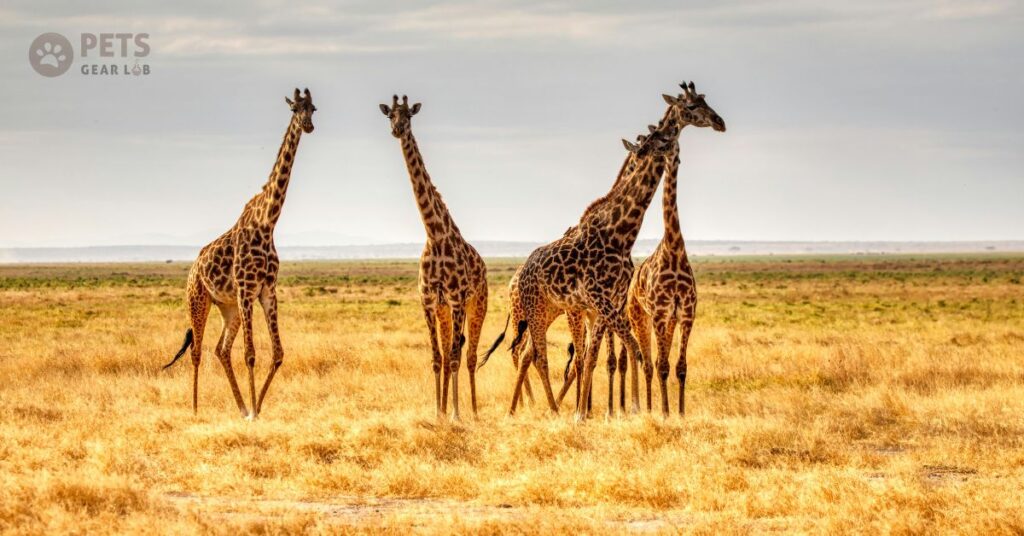

Giraffes, being the tallest land animals have a unique advantage they can reach parts of trees that no other species can access. This ability plays a crucial role in pollination and seed distribution, as well as in stimulating the growth of existing trees. Similar to rhinos and elephants, giraffes contribute to soil fertilization through their dung.
Additionally, giraffes serve as guardians of smaller animals by acting as an early warning system against predators. Their exceptional eyesight, they can detect carnivores like lions from great distances. When giraffes sense danger and start running, it alerts other prey animals to flee as well. This cooperative behavior promotes biodiversity, which in turn provides significant benefits for both humans and the planet at large.
5 Whales
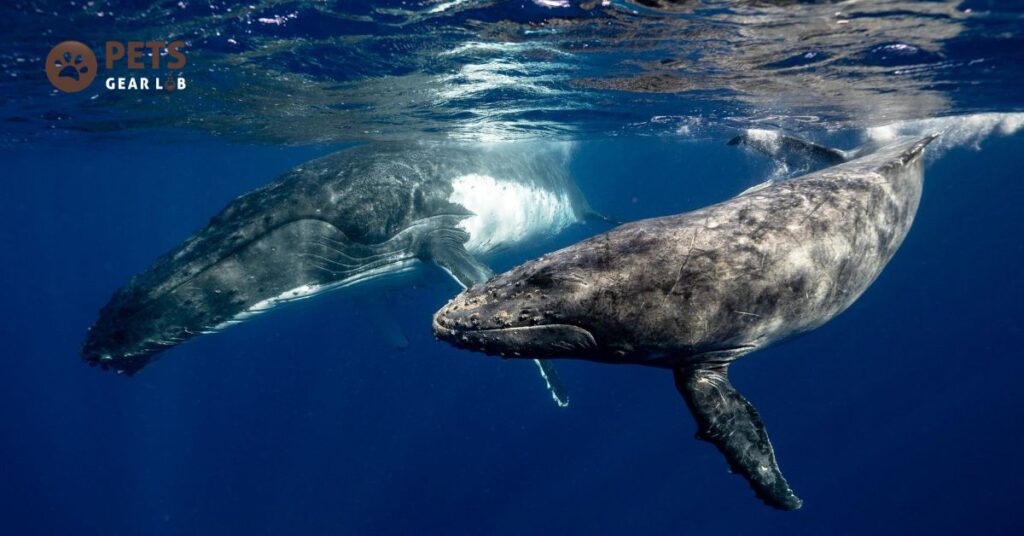

Whales play a critical role in providing a significant portion of the oxygen we breathe a fact that might surprise many. They accomplish this by supporting phytoplankton, tiny organisms resembling plants that reside near the ocean’s surface. Through the process of photosynthesis, phytoplankton absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, thereby aiding in the battle against climate change.
Whales primarily feed on various marine creatures like krill and fish, found deep within the ocean. Upon surfacing for air, they also release feces into the water. Interestingly, whale excrement acts as a natural fertilizer for phytoplankton, fueling their growth and enabling them to absorb hundreds of thousands of tons of carbon from the atmosphere annually. This emphasizes the crucial role of whales in mitigating climate change and underscores the importance of their conservation efforts.
6 Koalas
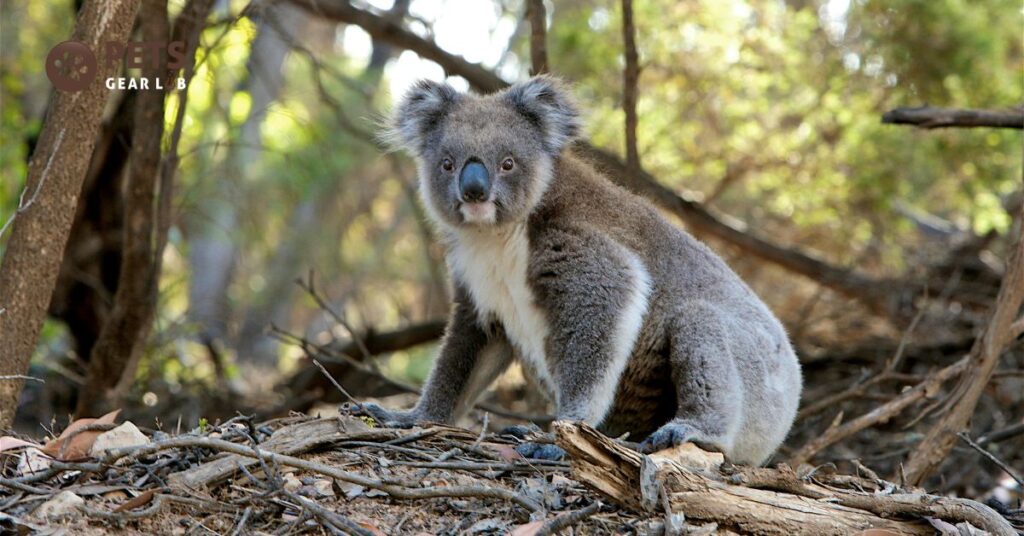

Koalas are key players in Australian ecosystems, serving various essential roles. Firstly, their droppings enrich the forest floor, promoting plant growth and supporting the diets of small mammals and insects. Secondly, birds use koala fur in their nests for its exceptional insulation properties.
Thirdly, koalas help maintain eucalyptus forests by preventing other animals from accessing these trees, thereby safeguarding crucial habitats. Protecting koalas isn’t just about their survival; it’s also vital for the countless plant and animal species that depend on them. With Australia facing frequent bushfires, conserving species like koalas, which contribute to ecosystem balance, becomes even more crucial for resilience.
7 Dogs

Dogs play a remarkable role in various aspects of human life, offering assistance and support in diverse settings. Therapy dogs, commonly found in homes, classrooms, nursing homes, and hospitals, are adept at alleviating stress and anxiety, providing invaluable comfort to individuals, particularly children with ADHD and autism.
In addition to therapy dogs, specially trained assistance dogs, known as service dogs in the US, offer personalized aid to individuals with disabilities, enhancing their independence and quality of life.
Moreover, dogs are invaluable assets in wildlife conservation efforts. Trained detection dogs, like those partnered with the University of the Sunshine Coast Detection Dogs for Conservation team in Australia, assist in locating injured or sick animals, such as koalas, aiding in health assessments and habitat surveys.
Furthermore, dogs demonstrate their heroic capabilities in disaster response scenarios. Davey the Spaniel, for instance, serves alongside the Lancashire Fire and Rescue Service in the UK, conducting search and rescue operations in the aftermath of earthquakes and explosions, locating individuals at high risk of being missing.
Notably, detection dogs also play a crucial role in combating wildlife crime by detecting shipments of animal parts, thereby contributing to efforts to curb wildlife trafficking. Dogs like Senseo and Sonic in Benin, as well as Bruce and Boris in jaguar poaching prevention, exemplify the significant impact dogs have in safeguarding our planet’s biodiversity.
8 Bats
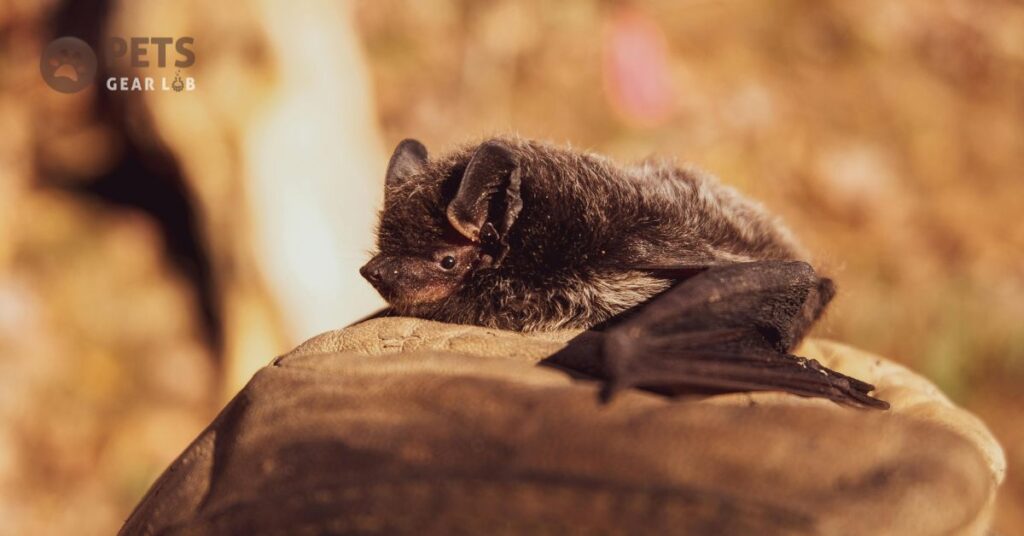

Bats, often associated with spooky imagery, actually play crucial roles in our ecosystem. Much like bees, butterflies, and birds, bats serve as pollinators. If you are a fan of bananas, mangoes, cashews, avocadoes, peaches, or figs, you owe a debt of gratitude to bats for pollinating their flowers and dispersing their seeds.
Moreover, bats are effective insect hunters, contributing to pest control by consuming mosquitoes, beetles, and moths. This not only helps prevent annoying mosquito bites and the diseases they transmit but also reduces the reliance on pesticides in agriculture. Additionally, bat guano, their manure, is a valuable source of nitrogen, enriching soil fertility and promoting healthy plant growth.
9 Sharks
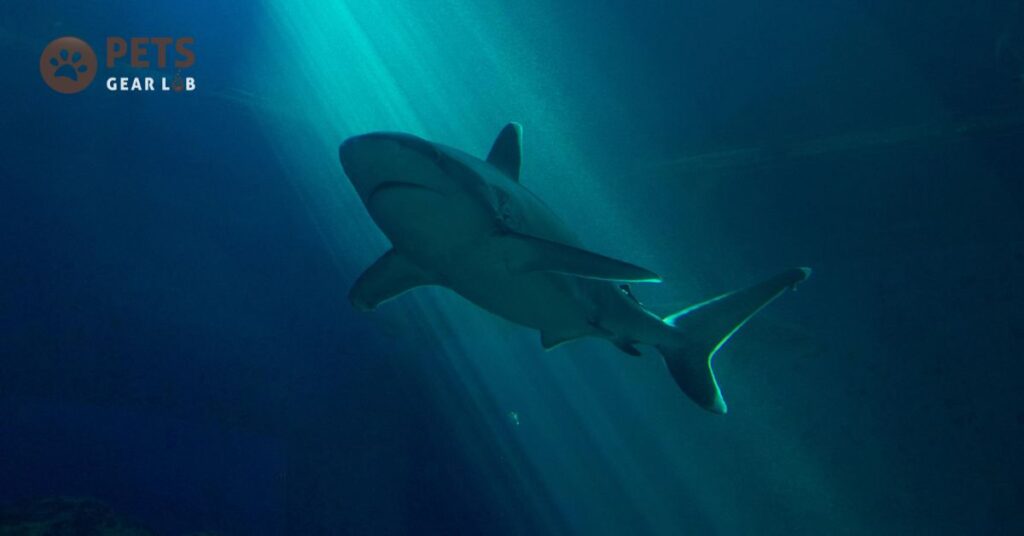

Despite their ominous reputation, sharks play indispensable roles in marine ecosystems, benefiting us in more ways than they pose threats. Their feeding habits influence the population and distribution of prey species, crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of oceanic ecosystems. Given that oceans are pivotal in mitigating climate change and producing approximately half of the world’s oxygen, preserving their health is paramount.
Sharks contribute to combating climate change by controlling the population of sea turtles, which, if left unchecked, could overpopulate and overgraze seagrass beds. Additionally, sharks regulate fish populations, indirectly safeguarding algae-eating fish, thus preventing algal overgrowth that could smother coral reefs.
Similar to whales, sharks play a role in nutrient cycling by dispersing nutrients from deep ocean waters to shallower regions through their fecal matter. This process aids in sustaining the health and productivity of marine ecosystems, highlighting the multifaceted importance of sharks in maintaining oceanic balance and biodiversity.
10 Bees
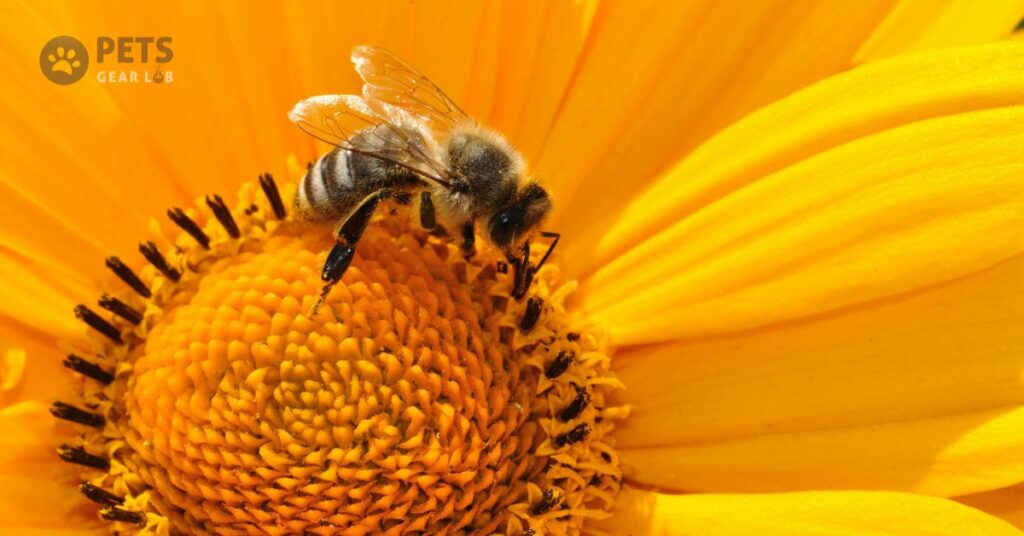

Bees, as pollinators, play a crucial role in our food production systems. About three-quarters of the crops we cultivate rely on pollinators, such as bees. If these insects were to disappear, crop yields would immediately decline by 5-8%. Honeybees, in particular, are responsible for pollinating around 80% of all flowering plants.
In addition to their pollination services, bees can also help mitigate human-wildlife conflicts. For instance, the International Fund for Animal Welfare (IFAW) recently implemented a beehive fence project in Malawi. These fences deter elephants, the largest land mammals, from encroaching too close to human settlements. Elephants avoid these tiny insects to avoid getting stung in sensitive areas like their eyes, ears, or trunks. Preventing such encounters is crucial, as they can quickly escalate into dangerous situations for both humans and elephants.
11 Primates
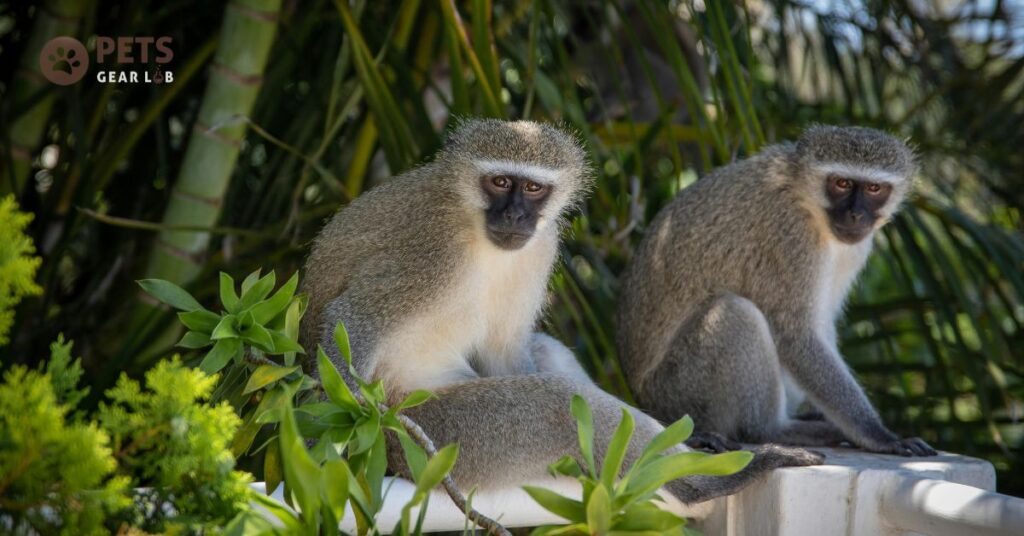

Protecting our closest animal relatives, the primates, is essential for several compelling reasons. Firstly, due to their striking similarities to humans, studying other primate species provides invaluable insights into our own behavior, biology, and evolution. Additionally, primates often play significant roles in promoting tourism and are integral to various cultural and religious beliefs in many regions.
Moreover, primates are vital components of their ecosystems. Their feeding habits contribute to seed dispersal, which in turn fosters plant growth and enhances biodiversity. Particularly noteworthy is their role in dispersing seeds of large-seeded tree species, which are crucial for carbon sequestration. By aiding in the dispersal of such seeds, primates actively contribute to mitigating climate change and preserving the health of our planet’s ecosystems.
12 Birds

Birds, much like bees, play crucial roles in ecosystems as pollinators and seed dispersers, contributing to the growth of plants used for food, timber, medicine, and recreation. Additionally, certain bird species help control insect populations based on their dietary preferences.
Birds of prey, such as hawks, eagles, kestrels, owls, and falcons, serve as top predators in the sky, regulating mouse and rat populations. This role is essential for preventing rodent overpopulation, which can pose health risks to humans. Vultures, on the other hand, act as nature’s sanitation crew by feeding on animal carcasses.
Birds also hold significance for researchers, who study their presence as indicators of ecosystem health and the effects of toxins. Moreover, birdwatching enthusiasts contribute to ecotourism by appreciating avian diversity in natural habitats.
Lastly, the guano (bird poop) of seabirds is rich in nitrogen and other nutrients, serving as an excellent fertilizer, thus highlighting yet another valuable contribution of birds to the environment.